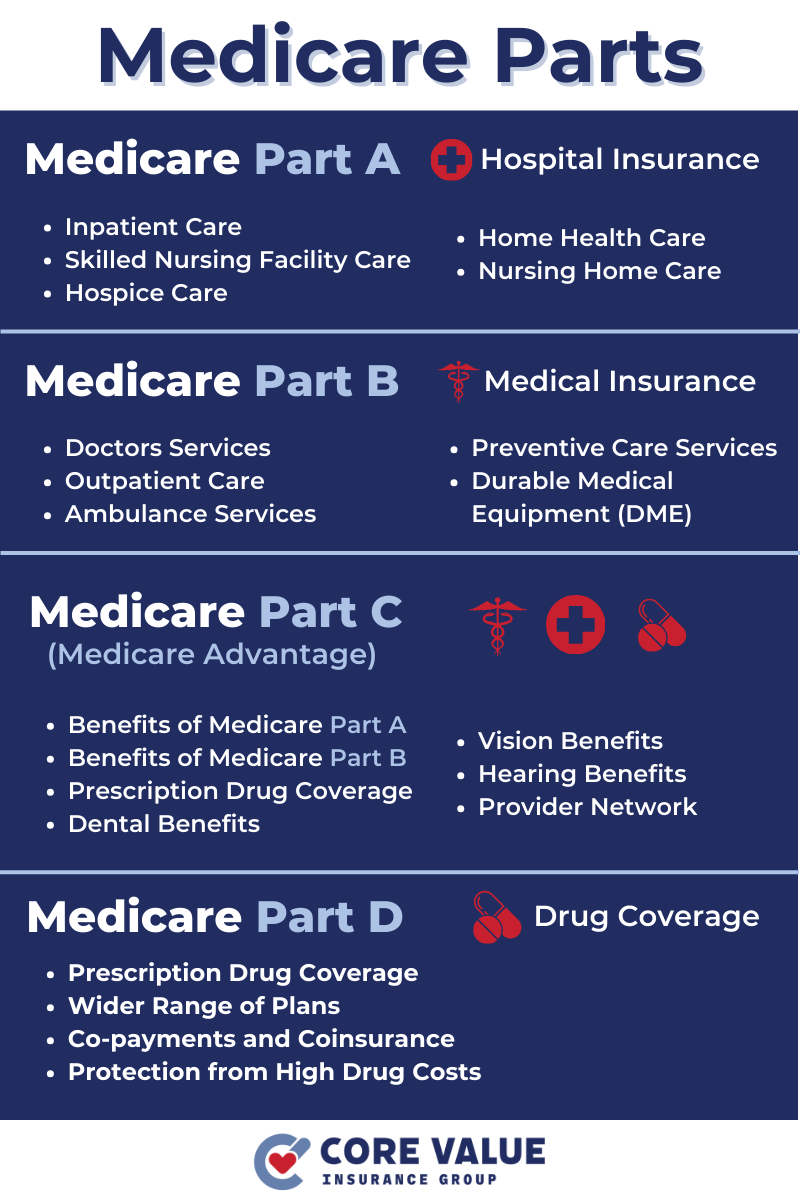
Medicare Parts play a crucial role in providing essential healthcare coverage for millions of Americans.
These parts, namely A, B, C, and D, offer various benefits and services to eligible individuals. Medicare coverage includes hospital stays, doctor visits, prescription drugs, preventive care, and more.
Each part serves a specific purpose and works together to ensure comprehensive healthcare support.
By exploring the different parts of Medicare, individuals can gain a better understanding of their options and make informed decisions about their healthcare plans.
Whether it’s Part A, Part B, Medicare Advantage (Part C), or Part D, knowing the details of each part is essential for navigating the complex world of Medicare effectively.
What is Medicare Part A?
Medicare Part A, also known as hospital insurance, provides coverage for inpatient care in hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, and some home health services.
It primarily focuses on services that require a stay in a healthcare facility. This includes hospital stays, hospice care, and limited skilled nursing facility care.
To be eligible for Medicare Part A, individuals must meet certain criteria. Most people qualify for premium-free Part A if they or their spouse have paid Medicare taxes while working for at least 10 years.
Those who don’t meet the criteria can still enroll but may have to pay a monthly premium.
Medicare Part A Enrollment Process
Enrolling in Medicare Part A is typically automatic for individuals who are already receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board benefits.
They will be enrolled in both Part A and Part B when they turn 65.
For those not automatically enrolled, they can sign up during their Initial Enrollment Period (IEP), which begins three months before their 65th birthday month and ends three months after.
The enrollment process can be done online through the Social Security Administration’s website or by visiting a local Social Security office.
It’s important to note that missing the Initial Enrollment Period may result in late enrollment penalties and delayed coverage.
Therefore, it’s crucial to understand the deadlines and take appropriate action to ensure seamless enrollment into Medicare Part A.
Understanding Medicare Part B
Medicare Part B, also known as medical insurance, covers a wide range of outpatient services and medically necessary supplies. It includes:
- Doctor visits
- Preventive services
- Lab tests
- Durable medical equipment (DME)
- Certain vaccinations
Part B is designed to ensure individuals have access to essential healthcare services outside of a hospital setting.
To be eligible for Medicare Part B, individuals must meet certain criteria. Most people are automatically enrolled in Part B if they’re already receiving Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board benefits.
However, those who aren’t automatically enrolled need to sign up during their Initial Enrollment Period (IEP).
Enrolling in Medicare Part B
Enrolling in Medicare Part B can be done online through the Social Security Administration’s website or by visiting a local Social Security office.
The IEP for Part B is the same as that for Part A – it begins three months before an individual’s 65th birthday month and ends three months after.
It’s important to enroll in Medicare Part B during the Initial Enrollment Period because delaying enrollment may result in late enrollment penalties and gaps in coverage.
Late enrollment penalties can increase the monthly premium for as long as an individual has Medicare.
Understanding the coverage provided by Medicare Part B and enrolling at the right time ensures individuals have access to necessary medical services without facing financial burdens.
What is Medicare Part C?
Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, offers an alternative way to receive Medicare benefits through managed care plans provided by private insurance companies.
These plans combine the coverage of Parts A and B and often include additional benefits such as prescription drug coverage, dental care, vision care, and fitness programs.
Medicare Advantage plans come with advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, they often have lower out-of-pocket costs compared to Original Medicare.
They may also provide coordinated care through a network of healthcare providers. However, these plans typically have restrictions on which doctors and hospitals can be used.
Medicare Parts
Speak with a licensed insurance agent!
Enter your Zip Code to View Medicare Plans in your Area
Speak with a licensed insurance agent!
Enter your Zip Code to View Medicare Plans in your Area
Part C Enrollment and Coverage
To enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan (Part C), individuals must first be enrolled in both Parts A and B of Medicare.
The enrollment process for Part C usually occurs during specific enrollment periods such as the Initial Enrollment Period (IEP) or the Annual Enrollment Period (AEP).
There are different types of Medicare Advantage plans available, including:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans
- Private Fee-for-Service (PFFS) plans
- Special Needs Plans (SNPs)
Each plan has its own network of providers and coverage rules.
When considering enrolling in a Medicare Advantage plan, it’s important to carefully review the options available in your area and consider factors such as cost, coverage, network size, and specific healthcare needs.
Understanding Medicare Part D
Medicare Part D is a prescription drug coverage program offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare.
It helps individuals with the costs of prescription medications, including both brand-name and generic drugs.
Part D plans vary in terms of the specific medications covered, so it’s important to choose a plan that aligns with your medication needs.
In addition to covering prescription drugs, Medicare Part D also provides protection against high drug costs.
This includes cost-sharing arrangements such as copayments or coinsurance, as well as coverage during the coverage gap (commonly known as the “donut hole”) and catastrophic coverage for those with exceptionally high drug expenses.
Choosing a Medicare Part D Plan
When selecting a Medicare Part D plan, it’s essential to compare different options available in your area.
Consider factors such as monthly premiums, annual deductibles, copayments or coinsurance amounts for your specific medications, and whether your preferred pharmacies are included in the plan’s network.
To make an informed decision, you can use the online tool provided by Medicare called “Medicare Plan Finder.”
This tool allows you to enter your current prescriptions and compare plans based on their estimated total annual costs.
It’s also crucial to understand the coverage gap (donut hole) and catastrophic coverage thresholds. The coverage gap is a temporary limit on what the drug plan will cover for prescription drugs.
Once you reach catastrophic coverage, you’ll pay significantly less for your medications for the rest of the year.
By carefully evaluating your medication needs and comparing different Medicare Part D plans, you can find one that offers comprehensive coverage at an affordable cost.
Make an Informed Decision
Understanding the different parts of Medicare is crucial for making informed healthcare decisions. Each part offers specific coverage that caters to different aspects of healthcare needs.
By enrolling in the appropriate parts based on individual requirements, individuals can ensure they have comprehensive Medicare coverage.
By knowing about Medicare Parts and their coverage options, you can navigate through the complexities of healthcare with confidence and make decisions that best suit your unique needs.
Speak with a licensed insurance agent!